Blogs
on June 28, 2024
In the intricate landscape of digital interactions, the safeguarding of sensitive data is paramount. This section delves into the methodologies and control your online presence guidelines essential for addressing breaches and vulnerabilities in online environments. It emphasizes the importance of timely and effective communication strategies when dealing with unauthorized access or data leaks.
Understanding the Implications: Every digital breach has the potential to compromise not only corporate integrity but also individual privacy. It is crucial to comprehend the far-reaching effects of such occurrences and the necessity to mitigate them swiftly.
Disclosure Protocols: Establishing clear procedures for reporting unauthorized access is vital. This involves creating a structured approach that encourages transparency and rapid response. Such protocols ensure that all stakeholders are informed and prepared to act decisively in the event of a security breach.
By integrating these strategies, organizations can enhance their resilience against digital threats and protect the integrity of their data and systems. This approach not only fortifies security measures but also builds trust among users and stakeholders.
Understanding Cybersecurity Incidents
This section delves into the critical task of discerning the potential hazards to confidentiality in digital environments. It is essential to recognize that the safeguarding of sensitive data is paramount in today's interconnected world. Here, we explore the various threats that can compromise the integrity of data and the measures that can be taken to mitigate these risks.
To begin with, it is crucial to understand the different types of risks that can arise in digital security. These can range from unauthorized access to data to the inadvertent exposure of sensitive details due to human error or system vulnerabilities.
Unauthorized Access: This occurs when an individual gains access to data without proper authorization. This can be through hacking, phishing, or exploiting system weaknesses. Data Breaches: These involve the intentional or accidental release of secure information to an untrusted environment. Malware Attacks: Malicious software can infiltrate systems, leading to data corruption or theft. Insider Threats: Employees or contractors with access to sensitive data can misuse their privileges, intentionally or unintentionally.
Identifying these risks is the first step towards developing effective strategies to protect data. It involves a thorough analysis of potential vulnerabilities within the organization's digital infrastructure and the implementation of robust security protocols.
Conduct Regular Security Audits: This helps in identifying potential weaknesses in the system. Implement Strong Access Controls: Limiting access to sensitive data can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access. Educate Employees: Regular training on security protocols and the importance of data protection can help prevent inadvertent breaches. Use Advanced Security Tools: Employing the latest in security technology can help detect and prevent attacks.
In conclusion, understanding the myriad of risks to data confidentiality in digital environments is essential for any organization. By proactively identifying these risks and implementing comprehensive security measures, organizations can protect their sensitive data and maintain the trust of their stakeholders.
Identifying Privacy Risks in Cybersecurity
This section delves into the critical task of recognizing potential threats to individual confidentiality within digital environments. It outlines strategies and tools necessary for identifying vulnerabilities that could lead to unauthorized access or exposure of sensitive data. Understanding these risks is essential for implementing effective safeguards and mitigating potential harms.
To effectively manage these risks, it is crucial to first categorize them based on their potential impact and likelihood. Below is a table that outlines common types of privacy risks and their descriptions:
Type of Risk Description Data Breach Unauthorized access or disclosure of sensitive data, potentially leading to identity theft or financial loss. Malware Infection Infiltration of malicious software that can compromise system integrity and user data privacy. Phishing Attacks Deceptive attempts to obtain sensitive information by masquerading as a trustworthy entity in electronic communication. Insider Threats Risks posed by individuals within an organization who misuse their access to sensitive information. Third-party Vulnerabilities Security weaknesses in services or products provided by external parties that can expose user data.
Each of these risks requires specific attention and mitigation strategies. For instance, data breaches may necessitate robust encryption and access control mechanisms, while phishing attacks might require enhanced user education and awareness. Insider threats often demand a combination of technical controls and policy enforcement to monitor and manage access rights effectively.
In conclusion, identifying privacy risks is a multifaceted endeavor that involves understanding the nature of potential threats, their sources, and the appropriate responses. By systematically addressing these risks, organizations can enhance their defenses and protect the confidentiality of user data in digital spaces.
Reporting Mechanisms for Cybersecurity Breaches
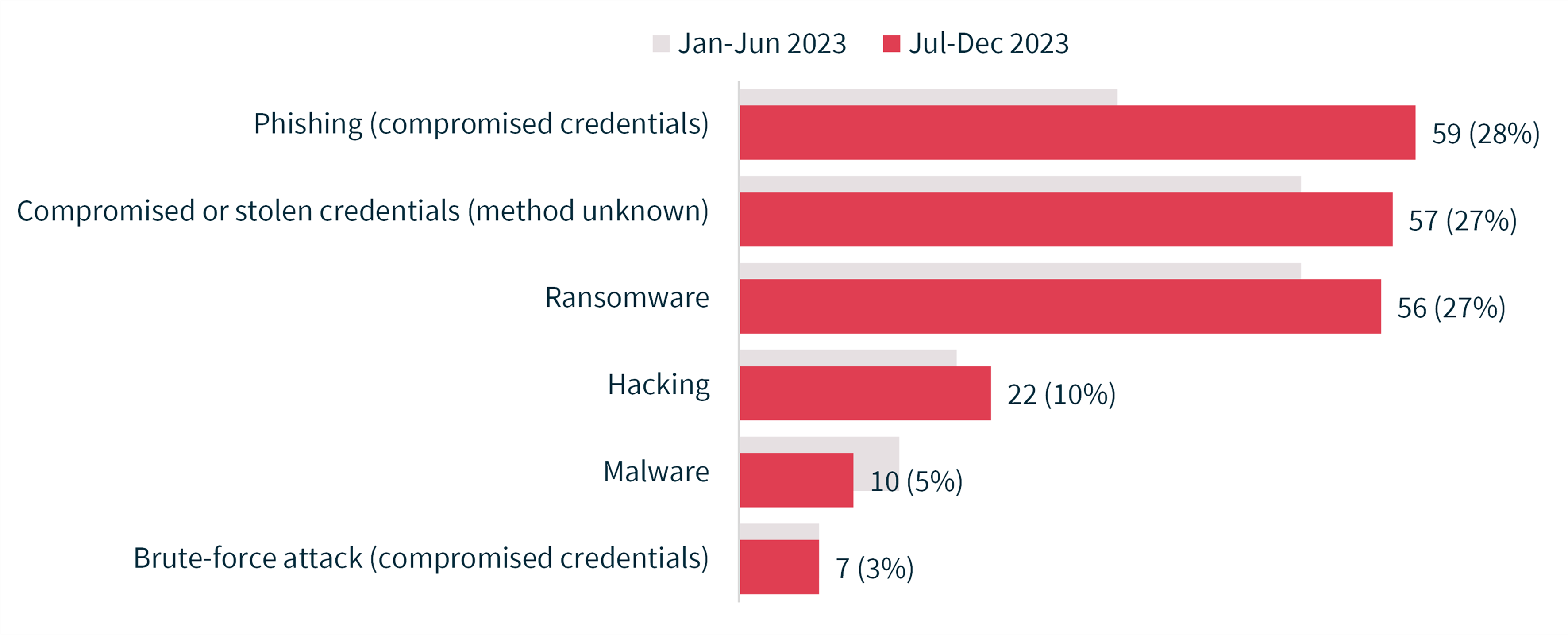
This section delves into the various methods and protocols organizations employ to address and communicate digital security failures. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for maintaining transparency and mitigating the impact of such events.
When a digital security breach occurs, swift and effective communication is paramount. Here are several key mechanisms used by organizations:
Internal Notification Systems: These systems ensure that all relevant internal parties are immediately informed of the breach. This includes IT departments, executive leadership, and potentially legal counsel. External Communication Protocols: Organizations must have clear strategies for informing external stakeholders, such as customers, partners, and regulatory bodies. This often involves issuing public statements or direct notifications. Legal Reporting Requirements: Depending on the jurisdiction and the nature of the breach, there may be legal obligations to report the incident to specific government agencies or regulatory bodies. Collaboration with Law Enforcement: In cases where criminal activity is suspected, working closely with law enforcement agencies is essential. This collaboration can help in the investigation and potential recovery of lost data or assets.
Implementing robust reporting mechanisms not only helps in managing the immediate aftermath of a breach but also in building trust with stakeholders and demonstrating a commitment to security and transparency.
Best Practices for Protecting Personal Information Online
In this section, we delve into the essential strategies and frameworks that govern the safeguarding of sensitive data in the digital realm. Understanding these legal requirements is crucial for maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of user data.
The digital environment is governed by a complex array of laws and regulations that aim to protect user data from unauthorized access and exploitation. These legal frameworks vary by jurisdiction but generally include provisions that mandate the secure handling of data, require notification in case of breaches, and enforce penalties for non-compliance.
One of the key aspects of these legal frameworks is the requirement for entities to implement robust security measures. This includes the use of encryption, secure authentication methods, and regular security audits to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities. Additionally, these frameworks often stipulate the need for clear and transparent privacy policies that inform users about how their data is collected, used, and protected.
Another critical component is the obligation to report any breaches of data security to the relevant authorities and affected individuals. This not only helps in mitigating the impact of breaches but also serves as a deterrent against lax security practices. The legal penalties associated with non-compliance can be severe, ranging from hefty fines to legal actions, which underscores the importance of adhering to these regulations.
Furthermore, these legal frameworks encourage the adoption of continuous education and awareness programs within organizations. This includes training employees on the latest threats and best practices in data protection, thereby fostering a culture of security awareness. By integrating these legal requirements into the organizational culture, entities can better protect the sensitive information they handle.
In conclusion, understanding and complying with the legal frameworks governing data protection is not just a legal obligation but a fundamental aspect of responsible digital citizenship. By adhering to these regulations, organizations can not only avoid legal repercussions but also build trust with their users, ensuring a safer digital environment for all.
Legal Frameworks Governing Cybersecurity Incident Reporting

Introduction: This section delves into the regulatory structures that oversee the disclosure of digital security breaches. It explores how various legal mandates shape the response and communication strategies following an online attack, ensuring compliance and safeguarding sensitive data.
Understanding Regulatory Requirements: Across different jurisdictions, the laws governing the reporting of network intrusions vary significantly. These regulations often dictate the timeframe within which entities must notify authorities and affected individuals about unauthorized access to their systems. Compliance with these laws is crucial not only for legal reasons but also to maintain public trust and operational integrity.
Key Legal Frameworks: In the United States, the Cybersecurity Information Sharing Act (CISA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union are prime examples of legislative measures aimed at enhancing digital security. These frameworks not only mandate reporting but also encourage the sharing of threat intelligence among organizations to foster a more robust defense against cyber threats.
Impact of Non-Compliance: Failure to adhere to these legal requirements can result in severe penalties, including financial sanctions and reputational damage. Moreover, it can lead to a lack of preparedness in dealing with future breaches, thereby exacerbating the vulnerability of affected entities.
Global Implications: As the digital landscape is interconnected globally, understanding and complying with international laws is essential for multinational corporations. This necessitates a comprehensive approach to legal compliance, which includes staying abreast of changes in cyber laws and adapting internal policies accordingly.
Conclusion: The legal frameworks discussed in this section underscore the importance of timely and accurate reporting of digital security breaches. They serve as a foundation for building resilient systems and processes that can withstand and respond effectively to cyber threats.
Tools and Resources for Effective Cybersecurity Incident Management

In this section, we delve into the essential instruments and materials that aid in the proficient handling of digital security breaches. The focus is on enhancing the capabilities of organizations to respond swiftly and effectively to any online threats, ensuring the integrity and safety of their digital assets.
Detection and Analysis Tools
One of the primary steps in managing digital security breaches is the timely detection and thorough analysis of the threat. Various software solutions are available that monitor network traffic and system logs for unusual activities. These tools use advanced algorithms to identify patterns that might indicate a breach, thereby enabling a prompt response.
Incident Response Platforms
Once a breach is detected, the next critical step is the response. Incident response platforms provide a structured framework for managing the breach, from containment to recovery. These platforms often include features like automated workflows, collaboration tools, and detailed reporting, which streamline the response process and ensure all actions are documented.
Training Materials and Workshops
Equipping staff with the right knowledge and skills is crucial in effective breach management. Training materials and workshops cover a range of topics, from basic awareness of digital security threats to advanced techniques in incident handling. Regular training sessions help keep the team updated with the latest threats and best practices in the field.
Legal and Compliance Resources
Understanding the legal implications and compliance requirements following a breach is essential. Resources such as legal guides, compliance checklists, and regulatory updates assist organizations in navigating the complex legal landscape. These tools ensure that all actions taken during the breach management process are compliant with relevant laws and regulations.
In conclusion, leveraging the right tools and resources is vital for managing digital security breaches effectively. By integrating these elements into their security protocols, organizations can enhance their resilience against online threats and protect their critical digital assets.
Training and Awareness Programs on Cybersecurity Incidents
In this section, we delve into the critical role of educational initiatives aimed at enhancing understanding and preparedness against digital threats. These programs are designed to equip individuals and organizations with the necessary knowledge to safeguard against online vulnerabilities and respond effectively to breaches.
Importance of Education: Educational initiatives play a pivotal role in mitigating the risks associated with digital breaches. By providing comprehensive instruction on how to identify, prevent, and manage attacks, these programs empower participants to take proactive steps in protecting their digital assets.
Types of Programs: There are various formats for these educational efforts, ranging from online courses and workshops to seminars and interactive simulations. Each format serves to engage participants differently, ensuring a broad spectrum of learning styles is accommodated.
Key Topics Covered: These educational programs typically cover a range of topics including the identification of common threats, understanding the importance of strong passwords, the use of encryption, and the implementation of multi-factor authentication. Additionally, they often include guidance on legal and ethical considerations surrounding data protection.
Impact on Organizational Security: Implementing robust educational programs within organizations can significantly enhance overall security posture. Employees who are well-informed about potential risks are less likely to inadvertently compromise security, thereby reducing the likelihood of successful breaches.
Continuous Learning: Given the rapidly evolving nature of digital threats, it is essential that these educational initiatives are ongoing and adaptable. Regular updates and refresher courses ensure that participants remain informed about the latest strategies and tools for defense against emerging threats.
In conclusion, investing in comprehensive educational programs is a strategic move for any entity looking to strengthen its defenses against digital attacks. By fostering a culture of awareness and preparedness, organizations can better protect their valuable digital assets and maintain the trust of their stakeholders.
Topics:
opt out whitepages
Be the first person to like this.





